Understanding addresses, public keys, and private keys are critical to understanding how bitcoin works.
- A wallet address is a randomly generated set of numbers and letters
- This set usually consists of 26 to 35 alphanumeric characters
- A wallet address is ideally a one-time link generated by a wallet
- Wallet addresses are needed to send or receive digital assets
- Digital assets are not actually stored in a wallet
- Public and private keys are needed to access a wallet address
- A wallet is where a collection of addresses is stored
- Never share your private key with others
The basic concept behind the two-key system is the following: the public key allows you to receive transactions, while the private key is necessary to send transactions. It gets a little bit more complicated when we take a look at how this ingenious system actually works.
Using two different keys (a public and a private key) is called asymmetric cryptography, which is a vital aspect of a blockchain. The two keys are connected to each other in mathematical terms.
The unique public key has its origins in the private key. This connection allows users to create unforgeable signatures, which can only be validated by other participants of the network who have knowledge of the corresponding public key.
Using two different keys - a public and a private key - is called asymmetric cryptography.
There are a lot of misconceptions regarding the differences between addresses, keys, and wallets. To provide more clarity on this topic, let’s look at their characteristics one by one.
Address
An address is a randomly generated set of numbers and letters which represent a type of unique number similar to a bank account number. As an example, here is the Bitcoin genesis address - the first Bitcoin address ever: 1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa.

The difference is that an address can be created for free by anyone and within a matter of seconds without needing a third party. You can create as many public addresses as you like or need.
You can freely share your public address with others. That way, people can send bitcoins to your address.
Because the Bitcoin network is not anonymous but pseudonymous, your holdings and transactions can be viewed by anyone who knows your public address.
Keys
There are two types of keys: public keys and private keys. Public keys are comparable to account numbers. They can be freely shared with everyone, and anyone can potentially send transactions to them.
Private keys, on the other hand, should be kept private, as their name suggests. You can think of them as a kind of PIN or verification code, which, together with its corresponding public key grants you access to the actual funds on the blockchain.
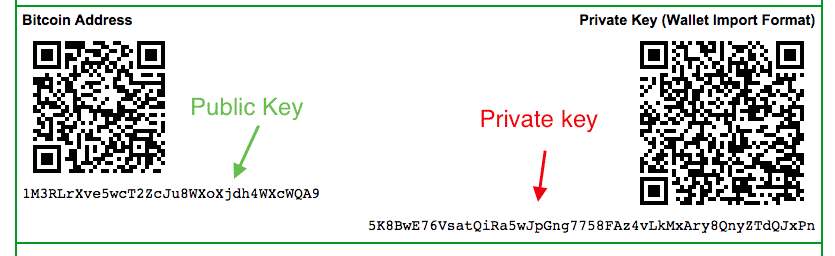
You should NEVER, under any circumstances, share your private key(s) with any other person. It’s best to store them in the most secure way possible (e.g. on a paper wallet or a hardware wallet).
Note that the keys are not stored on a blockchain. Instead, they can be kept in an (encrypted) file, which can be saved anywhere and stored offline.
Wallet
You can think of a wallet as a sort of encrypted virtual keychain, containing all the information needed to access your funds on the Bitcoin blockchain. A wallet combines and contains both your address(es) as well as your digital key(s).
The simplest form of a wallet is a file containing a database. It can also be stored offline because it does not need a connection to an actual blockchain.

Sovereign Monk
Bitcoin, Privacy & Individual Sovereignty Maximalist | Founder of European Bitcoiners - for Free and Open Bitcoin Education.
follow me :




Related Posts
How does Bitcoin Mining Work?
Jul 05, 2025
7 Bitcoin Scams You Need To Be Aware Of
Jul 05, 2025
What is Bitcoin?
Jan 16, 2025